We Are Open For Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Treatment in Gurgaon!
Fill the form and let us call you back.
[gravityform id="3" title="false" description="false"]
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) Treatment at Physioheal Physiotherapy, Gurgaon
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome – Introduction
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) and its effective physiotherapy management at Physioheal Physiotherapy one of the best physiotherapy center in Gurgaon. Dive into the details of CTS, including its symptoms, causes, diagnosis, treatment options, and the crucial role that physiotherapy plays in alleviating its effects.
Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is an entrapment neuropathy caused by compression of the median nerve as it travels through the wrist’s carpal tunnel. Normal tissue pressure within the tunnel is approximately 3-7mm Hg. CTS can result in pressure with greater than 30mm Hg.
It is the most common nerve entrapment neuropathy, accounting for 90% of all neuropathies.
Early symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome include pain, numbness, and paresthesias. Sensory changes and paresthesia along with median nerve distribution in Hand. Symptoms typically present, with some variability, in the thumb, index finger, middle finger, and the radial half (thumb side) of the ring finger. Pain also can radiate up the affected arm. Radiate into upper extremity, shoulder and neck. With further progression, night pain, hand weakness, decreased fine motor coordination,decreased grip strength, clumsiness, reduced wrist mobility and thenar atrophy can occur.
The prevalence of carpal tunnel syndrome is estimated to be 2.7-5.8% of the general adult population, with a lifetime incidence of 10-15%, depending on occupational risk 4.
Carpal tunnel syndrome usually occurs between ages 36 and 60 and is more common in women, with a female-to-male ratio of 2-5:1.
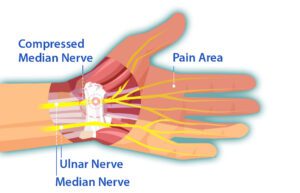
Symptoms of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS)
CTS is an entrapment neuropathy resulting from the compression of the median nerve within the wrist’s carpal tunnel. Early symptoms include pain, numbness, and paresthesias. These sensations typically manifest in the thumb, index finger, middle finger, and the radial half of the ring finger. As CTS progresses, symptoms can extend into the arm, shoulder, and neck. Night pain, hand weakness, decreased fine motor coordination, grip strength reduction, clumsiness, restricted wrist mobility, and thenar atrophy may also occur.
Causes and Prevalence of CTS
CTS arises from the compression of the median nerve within the carpal tunnel. The tunnel is surrounded by wrist bones and a sturdy ligament. Factors like genetic predisposition, repetitive wrist movements, obesity, diabetes, cumulative trauma disorders, hypothyroidism, and more contribute to CTS development. Its prevalence ranges from 2.7% to 5.8% of the adult population, occurring more frequently in women aged 36 to 60.
Diagnosing Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS)
Diagnostic tools for CTS include ultrasound, MRI, and electromyography (EMG) nerve conduction studies. Imaging methods help identify nerve compression and anatomical variants. EMG studies confirm the diagnosis and assess the severity of nerve signal transmission. Clinical exams assist in ruling out other conditions. X-rays are useful to exclude other wrist pathologies.
Physiotherapy’s Essential Role in CTS Treatment
Patients with mild to moderate symptoms can be effectively treated in a primary care environment. Physiotherapy is important in the treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome. Your physiotherapist can confirm your diagnosis and establish its severity. To establish a diagnosis a special nerve conduction test may be required to assess the transmission of signals along the affected nerve. From the assessment, your physiotherapist will devise an appropriate treatment plan. Treatment often involves involve activity modification, the taking of anti-inflammatory medications, electrotherapy and splinting of the wrist and hand. Often simple obvious alterations to the working practice can be beneficial in controlling milder symptoms of CTS. Other treatment options include:
- Soft Tissue Treatment
- Taping
- Proprioceptive Exercise
- Postural Realignment
- Ergonomic Assessment
Manual therapy techniques include mobilisation of
- Soft tissue
- Carpal bone
- Median nerve
Surgical Considerations and Post-Surgery Physiotherapy
Severe or chronic cases may require surgical intervention. After surgery, active physiotherapy is essential for full hand function restoration. Physiotherapy focuses on strengthening the hand, restoring wrist and hand range of motion, and desensitizing the scar tissue.
Effective CTS Management with Physioheal Physiotherapy
For comprehensive CTS treatment, consult Dr. Divya Gaur at Physioheal Physiotherapy Gurgaon. Dr Divya is one of the best physiotherapist in Gurgaon. Our expert physiotherapists collaborate closely with you to devise a tailored rehabilitation plan. To book an appointment, call +91-9999259307, book online, or request a phone consultation.
